Networking Scales AI Compute for Future Demand
Relentless Demand Drives Compute Infrastructure Overhaul
Despite public discussion of an "AI bubble," massive infrastructure commitments from major technology companies confirm that the race for superior Artificial Intelligence (AI) compute is in full swing. Check the recently news, Microsoft announced the largest and most sophisticated AI data center in Wisconsin, Fairwater, alongside plans for investments in AI data centers in Norway and the UK. And OpenAI signed a five-year cloud computing agreement with Oracle, reported to be worth $300 billion for compute capacity starting in 2027. And significantly more investment is believed to be coming, the immense scale of modern large language models (LLMs) is the primary driver.
Consider the exponential growth: the largest current language models are estimated to be over 1.5 trillion parameters, a nearly 10-fold increase compared to GPT-3.0's 175 billion parameters. This massive scale directly translates into extreme memory requirements:
• Model Inference (running the trained model) requires roughly 2 to 6 TB of memory.
• Model Training (building the model from scratch) requires even more, exceeding 20 TB of memory.
Since no single XPU (accelerated processing unit) has the memory capacity to handle such vast data amounts, AI work must be strategically partitioned and distributed across multiple XPUs. This necessity mandates two distinct, yet complementary, networking strategies: Scale-Up and Scale-Out.
The Dual Approaches: Scale-Up and Scale-Out
We have talked about how the AI workload works and how to use Ethernet to optimize the AI workload in previous blogs series (Series 1 & Series 2). Today, let's explore how we can extend the XPU cluster scale to support the exponential growth of computing demands.
To make the concept easy to understand, imagine you are running a logistics business. To improve transport efficiency, you can either upgrade individual vehicles to carry more load (Scale-Up) or hire more trucks to deliver packages in parallel (Scale-Out). The industry employs a two-pronged strategy to extend the scale of XPU clusters, combining both approaches based on business expansion strategy.
1. Scale-Up Networks (Upgrading the Vehicle)
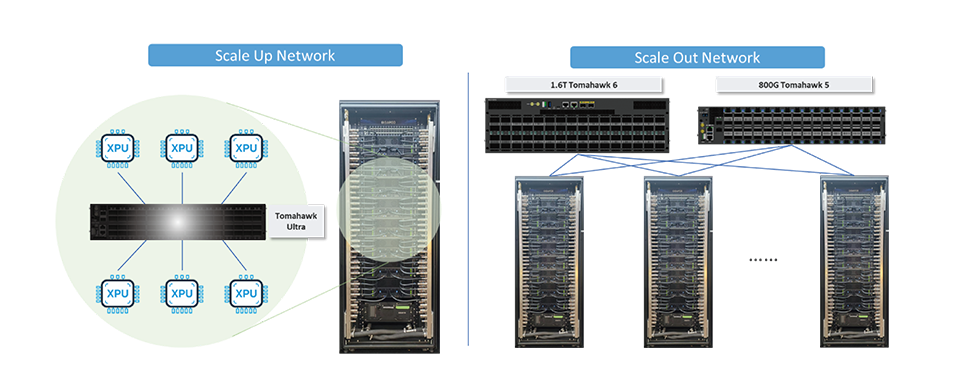
Scale-Up is the foundational step, focusing on building a large, virtualized XPU by interconnecting accelerators within a single domain (like a single server or rack) using ultra-high-speed, low-latency connections.
• NVIDIA's NVLink is the established technology here. It achieves high-speed XPU-to-XPU communication and a unified memory pool by interconnecting up to 72 XPUs via the NVLink Switch System.
• However, the industry is moving towards open standards to reduce vendor lock-in:
Ultra Accelerator Link (UALink): A direct competitor to NVLink , UALink is supported by major players like AMD, Intel, Microsoft, and Meta. The v1.0 specification provides 200G per lane connections for up to 1024 accelerators.
Scale-Up Ethernet (SUE): Broadcom proposes an Ethernet-based Scale-Up approach. Their Tomahawk Ultra chip is optimized for XPU-to-XPU communication. It maintains full Ethernet compliance while offering features like 250ns switch latency and a high-performance, lossless fabric.
2. Scale-Out Networks (Hiring More Trucks)
Scale-Out is the next logical step, which involves interconnecting multiple individual virtual XPU nodes (the Scale-Up units) into a massive cluster to increase total compute power in parallel. The Scale-Out network generally uses RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) to realize direct memory access between XPU nodes in different racks. The main protocols used are Infiniband and RoCEv2 (RDMA over Converged Ethernet).
While Ethernet is ubiquitous, its traditional "best-effort" design is not optimal for the extreme scale, efficiency, and reliability demanded by AI training. This led to the formation of the Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC). UEC's goal is to deliver an open, interoperable, high-performance, full-communications stack based on Ethernet to meet the stringent requirements of AI and HPC at scale.
Conclusion: UfiSpace's Leadership in Open AI Networking
For decades, the Data Center market has pioneered high-speed network adoption. With the rise of AI/ML, this pace is accelerating, and the scale is becoming dramatically larger.
The industry's collective push toward open and scalable Scale-Up and Scale-Out solutions is a necessary response to avoid single-vendor lock-in. This shift is where UfiSpace steps up.
UfiSpace is actively facilitating this innovation by offering cutting-edge solutions built on the Ethernet architecture. Our commitment to next-generation AI networking is clear: our 800G platforms are ready now, and we are actively tracking the development of our 1.6T platform and the Scale-Up Ethernet solution with Tomahawk Ultra. We are dedicated to ensuring the future of AI networking is built on open, high-performance, and vendor-agnostic infrastructure.
Contact us to find out more about our offerings.
About the Author
 |
Will Chang Will Chang, Technical Marketing Manager at UfiSpace, provides technical expertise and executes marketing campaigns on technical topics. |
