Using OpenBNG to Build Resilient Broadband Networks
by Victor Khen

In a post-pandemic world, many countries understood their dependence on ubiquitous high-speed broadband coverage and encouraged more initiatives for the development of fixed broadband networks.
Communication Service Providers (CSP) are looking to maximize ROI from new broadband infrastructure and try to build networks more futureproof. Some view broadband networks as a potential platform for the introduction of fixed-mobile convergence (FMC), a consolidation of broadband and mobile networks that will bring ultimate efficiency and cost optimization, and provide capacity to support ever-growing traffic and new services.
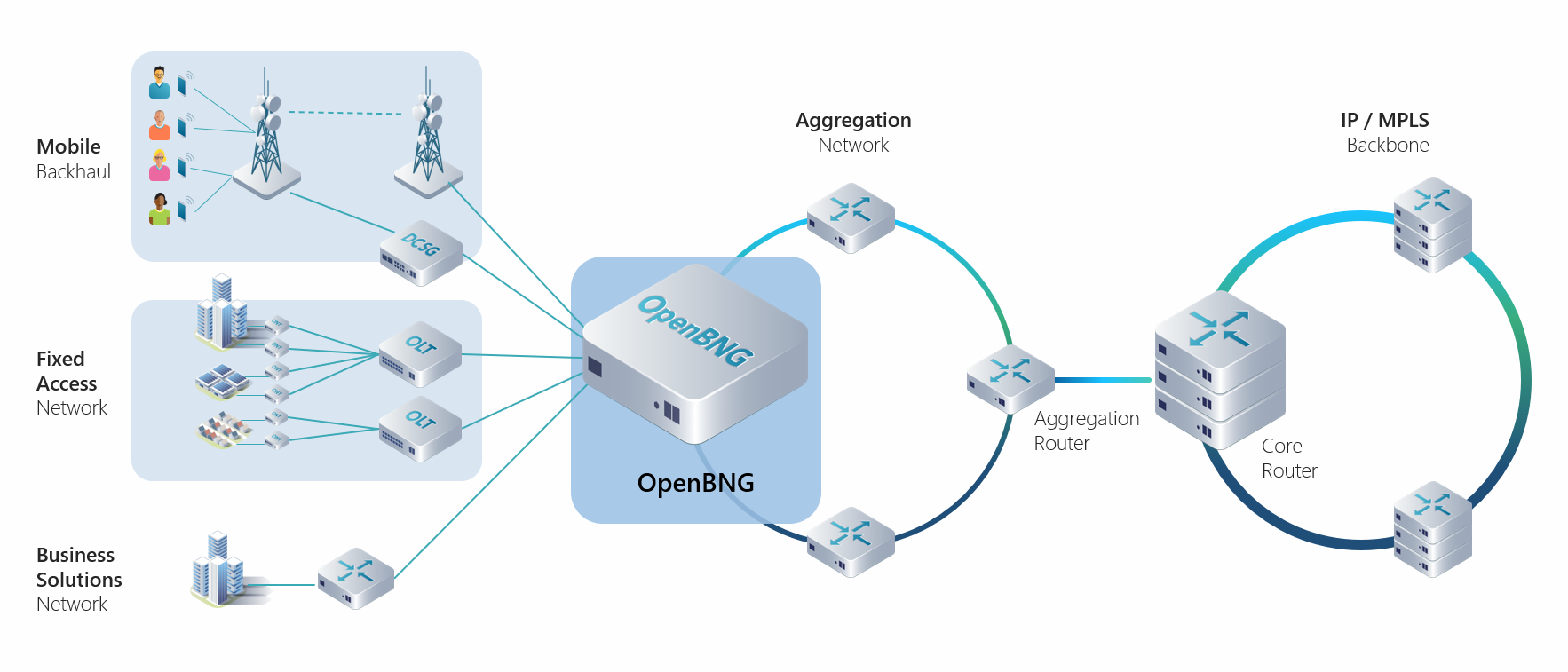
OpenBNG deployment in aggregation network
In every way, we will see much higher workloads on broadband infrastructure. In this blog, we outline and explain one of the latest trends in the development of broadband networks – open broadband network gateways (OpenBNG) and how they will improve the reliability of broadband networks.
Disaggregation of BNG and its benefits
To have a clear understanding of OpenBNG resilient models, let’s first overview the major architectural changes and functions split introduced by Broadband Forum for OpenBNG:
Disaggregating the broadband network gateway (BNG) brings unprecedented flexibility in the selection of best-optimized hardware and software for BNG network build-outs to avoid dependency on a single vendor's roadmap. OpenBNG is generally composed of white box hardware, an open network operating system (NOS), and various network service applications.
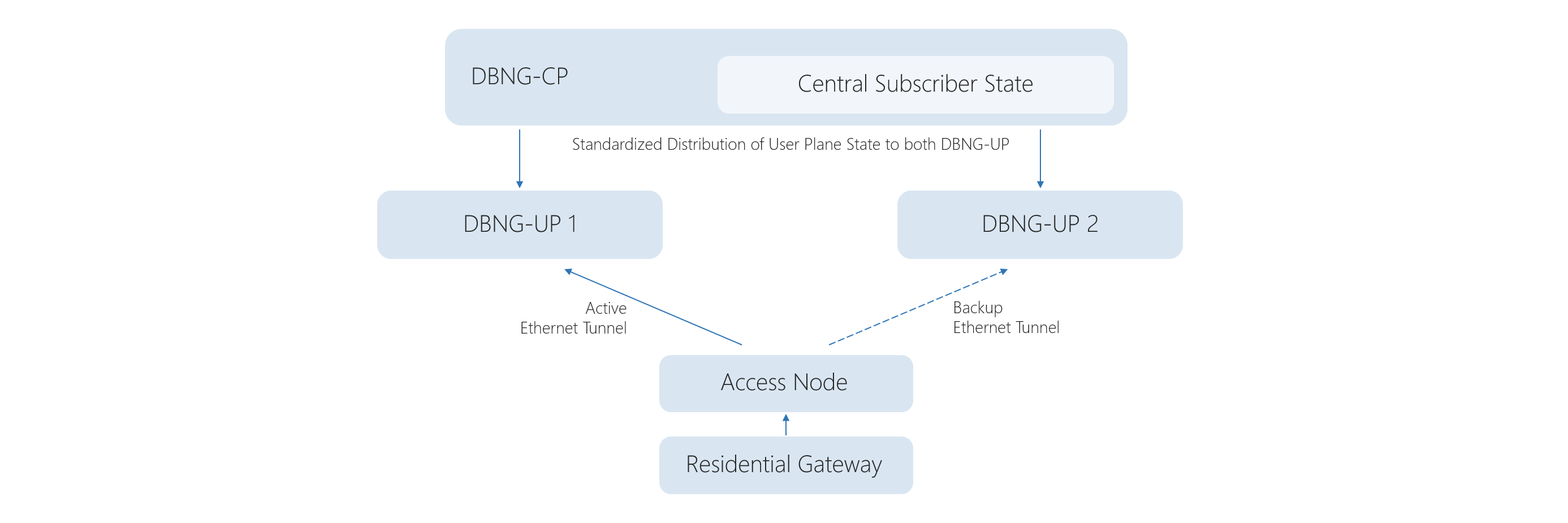
The separation of the control plane (CP) and user plane (UP) (TR-459) introduces a converged control plane that communicates with residential and business gateways across various user planes using standardized interfaces, and the master's subscriber state is responsible for sending the required forwarding and QoS to each user plane. The approach provides unified subscription management, seamless billing, and charging. It also offers centralized control over session management and authentication of endpoints (UE, 5G-RG, FN-RG). Aside from functional benefits, the approach also brings significant benefits to network resiliency and management: allows to distribute BNG functions across the network; offers zero-touch-provisioning (ZTP); introduces centralized management and streamlined failover mechanisms.
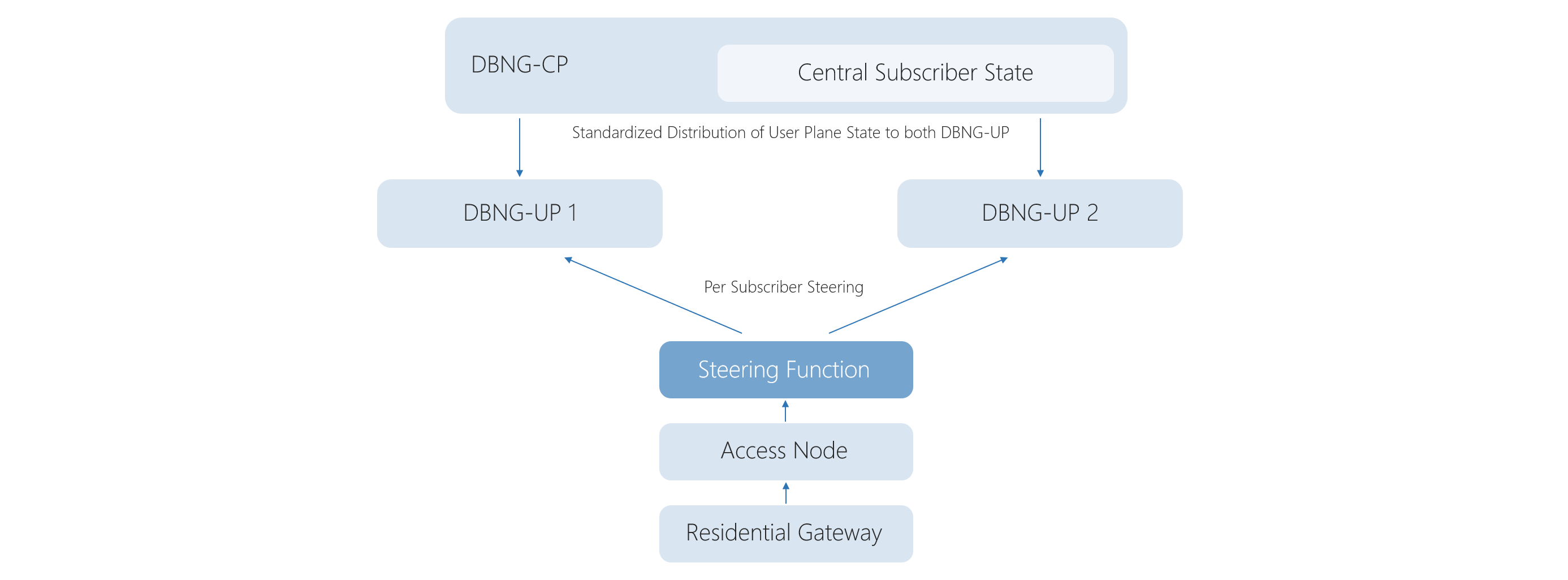
Subscriber session steering (TR-459) dynamically configures the network and can redirect any subscriber or a group of subscribers to any reachable UP. It allows to create the best optimized BNG networks that offer higher capacity utilization with decreased downtime.
OpenBNG deployment models and their resiliency
There are three major OpenBNG deployment models proposed by Telecom Infra Project (TIP) OpenBNG technical requirements.
Standalone model delivers deployment simplicity and highest cost optimization, especially when compared to traditional chassis-based BNG solutions.
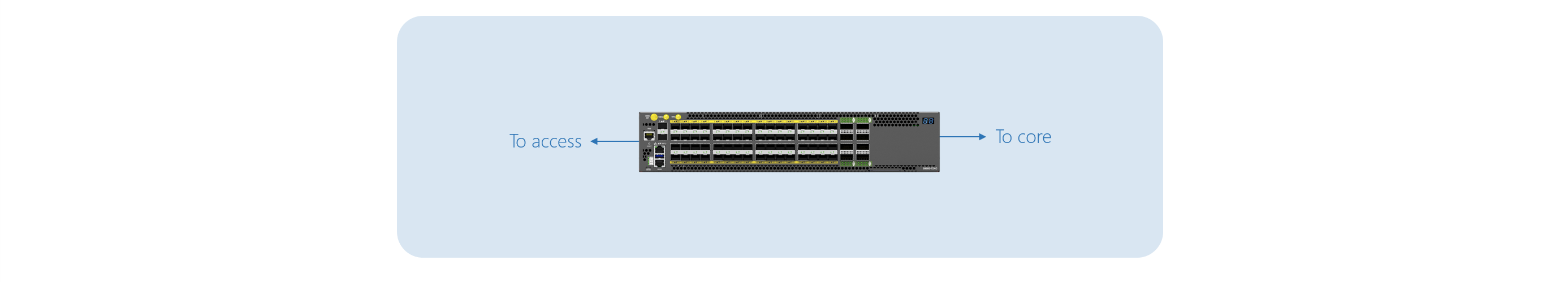

Standalone OpenBNG deployment model
In the standalone model, operators can deploy a single BNG instance within a multi-service open aggregation router (for ex. UfiSpace S9600 Series). The OpenBNG will provide all the BNG features and can later be scaled by adding additional servers for computing resources to run more complex applications at the edge (for ex. BNG sessions, PE services, timing/synchronization, etc.). Also, through the deployment of additional OpenBNG nodes, evenly dividing links towards access downstream nodes and subscriber sessions, CSPs can scale network and subscriber capacity; each BNG in this scenario will serve as a subset of a downstream access network.
The standalone deployment model does not provide service failover to other OpenBNG nodes within CSP's network and relies solely on component redundancy of the hardware platforms (ex. redundant PSUs, fan modules, etc.). However, due to the flexibility of available OpenBNG NOS, the standalone deployment model can generally be configured to the cluster model.
Cluster model can introduce additional benefits such as high resilience, decreased downtime, and load balancing.
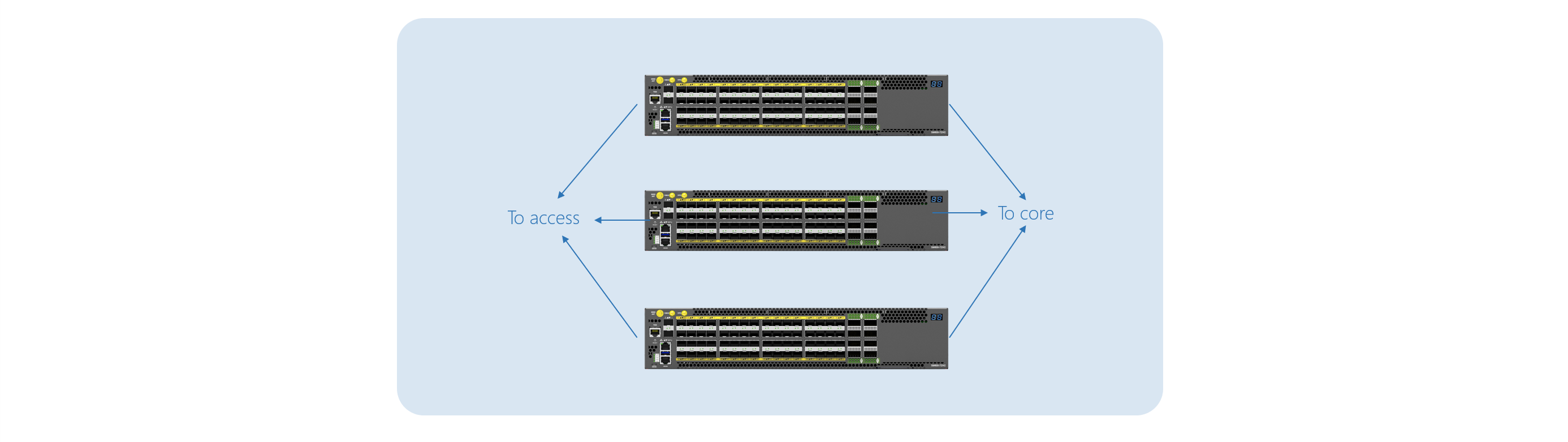
Cluster OpenBNG deployment model
OpenBNG cluster deployments consist of 2 or more BNG nodes that are interconnected for failover and advanced workload optimization between the nodes (ex. load balancing). The cluster model can be scaled just like a standalone with the addition of servers and BNG nodes.
With the deployment of the cluster model, CSPs can enjoy the full benefits of control and user planes separation. The OpenBNG cluster can be deployed in an active-passive configuration; in this case, CP will monitor and failover traffic between UPs providing automated network resilience. The CP can be initiated on a dedicated server hardware or each OpenBNG node, depending on NOS configuration. UP is intended to be initiated on BNG nodes.
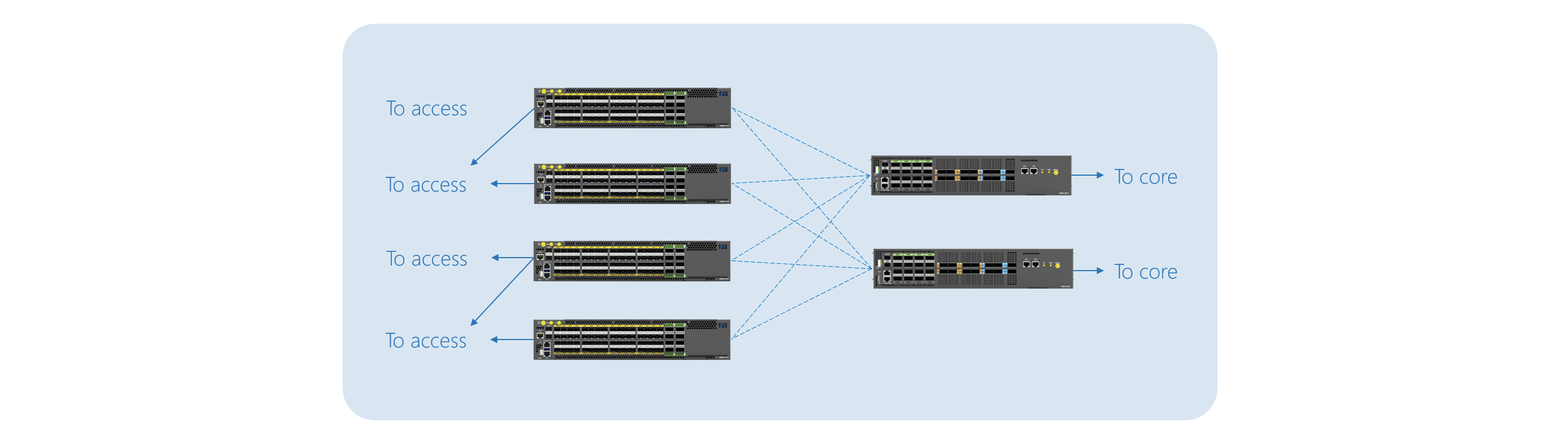
Spine-and-Leaf OpenBNG deployment model
The spine-and-Leaf BNG resiliency model adopts a data center approach for building high-capacity networks. The high-capacity network nodes (ex. S9600-32X, S9600-64X, S9600-30DX) with 100/400G uplinks and 25/100G downlinks are deployed as spine nodes, and lower capacity nodes (ex. S9600-72XC, S9500-30XS) with 25/100G uplinks and 1/10/25G downlinks are deployed as leaf nodes. Due to modern NOS development, the whole architecture can be recognized as one high capacity BNG node, which significantly simplifies network management and provisioning of new services.
The function split between CP, UP, traffic steering, and various add-on services is managed by NOS across the spine-and-leaf cluster. The deployment model offers maximized resources for load balancing, multi-service provisioning, ultimate scalability, and simplified network management. It is currently being tested and adopted by several major international broadband operators.
In this blog we have reviewed three OpenBNG resiliency models that can help operators to build best optimized, sustainable networks, to offer high quality of service today; easily adopt new services tomorrow, and ensure high ROI along the journey.
For more information about UfiSpace's Open BNG solutions, please contact our sales team.