[英文] Optimize Network Efficiency with FlexE
by Will Chang

Recent study from GSMA showed that the pace of adopting 5G is faster than its previous generations (3G and 4G). Just 18 months after launch, 5G took a 5.5% share of connections versus the 2.2% for 3G and 4G respectively within the same period after launch.
With such a fast adoption rate, new services promised by 5G may come earlier than expected and not just high speed connectivity, consumers can also expect a better service experience and quality.
To fulfill the demand, operators need a more intelligent, flexible and efficient network infrastructure. Flexible Ethernet (FlexE) is a technology that extend the capabilities of Ethernet to solve the challenges of a rapidly growing network. Let’s take a look at these challenges and how operators could benefit from adopting FlexE.
Ethernet Limitations Leading to FlexE
The Ethernet dominates the transport network today and the standard is maintained by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). It has a fixed data rate standard with various iterations of speeds such as 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps, 25Gbps, 40Gbps, 50Gbps, 100Gbps, 400Gbps, all the way to 800Gbps. Compared to previous network technologies, the designs of Ethernet have brought benefits like low cost, simplicity and reliability, which made it spread widely across every segment of network.
With that being said, Ethernet has also hit a bottle neck when we are trying to accommodate to today’s explosive digital world. The demand on capacity growth is faster than expected. Although Ethernet has different speed options, it’s still limited when compared to other standards like DWDM, which can support varying data rates in increments of 25Gbps.
Different applications like video streaming, conference calls, IoT and autonomous driving will need different transport policies to meet its requirements. That led to the need for network slicing. FlexE is designed to extend the existing Ethernet and provide more flexibility to support those use cases on the physical level.
What is FlexE (Flexible Ethernet)?
Flexible Ethernet, or FlexE, enables more flexible Ethernet connections by introducing features to break the limits bound by current Ethernet standards.
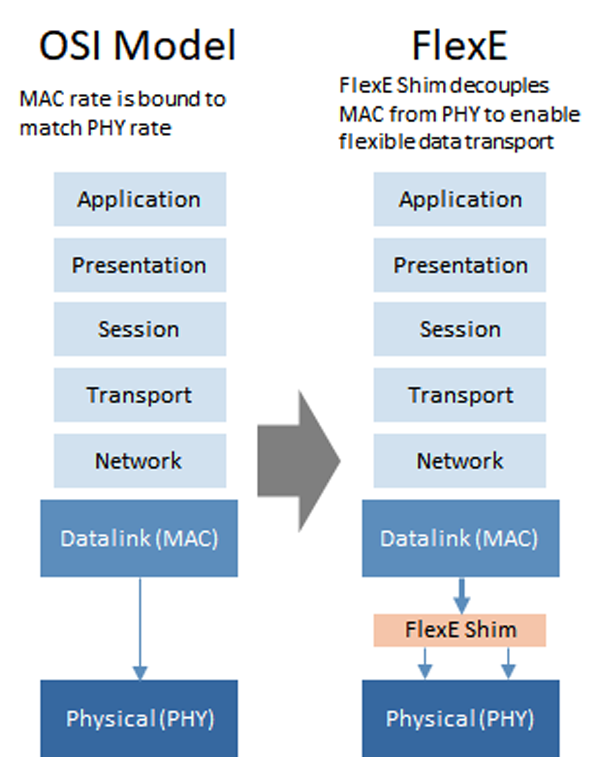
FlexE adds Shim between MAC and PHY to enable flexible data transport
By inserting an extra layer called, Shim, into the traditional Ethernet stack between the MAC and PHY, FlexE can decouple the MAC and PHY layers to enable more flexibility for data manipulation.
The Shim uses a mechanism called, Calendar, which divides the transport resource into 5Gbps slots. Data stream is filled into these slots and distributed over the physical interface. The functionalities of the FlexE Shim are:
• Perform multiplexing and demultiplexing of data blocks between MAC and PHY
• Manage data block scheduling and distribution into the Calendar slots
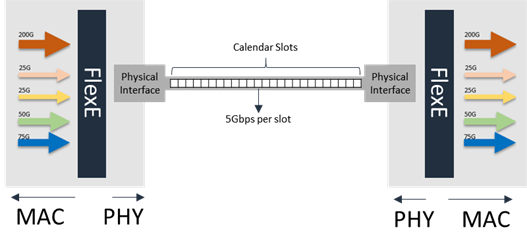
FlexE Shim breaks data stream into 5Gbps calendar slots
With the help of the FlexE Shim, Ethernet data stream is no longer a fixed rate and bound to a physical interface. Data can be processed in finer granularity (5Gbps) and distributed cross multiple interfaces. It also enables the following functions and helps service operators overcome the challenges to meet higher transport bandwidths, flexible data rates and customized services policies:
• Bonding: Create a higher bandwidth virtual interface with multiple lower bandwidth physical interfaces
• Sub-rating: Create a lower bandwidth data stream
• Channelization: Create multiple channels in a physical interface
Let’s take a closer look at these FlexE features.
Features of FlexE
Bonding
Bonding utilizes multiple physical interfaces to create a virtual data pipe with a higher bandwidth. Operators could leverage lower speed routers and optics to support higher data rates. For example, two 400GE ports could be bonded together to form a 800GE virtual data pipe to provide higher bandwidth transport.
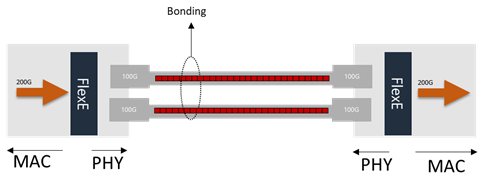
FlexE Bonding example
Sub-rating
FlexE Sub-rating creates a lower rate data stream by marking unused slots as unavailable. This allows a router to deliver data with rates other than the specific data rate defined by Ethernet standards. Thus, optimizing fiber utilization because it can match the data rates of the transport network equipment. For example, to match a transponder configured to deliver data in the non-standard Ethernet rate of 75Gbps, FlexE can create a 75Gbps data stream using a 100Gbps interface. Without FlexE, we can only transmit in standard data rates like 40Gbps, which results in bandwidth underutilization.
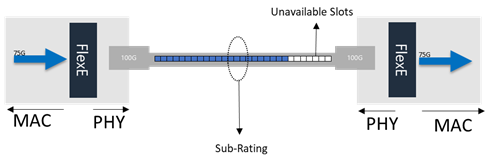
FlexE Sub-rating example
Channelization
Channelization distributes different data streams into the calendar slots and creates logical channels for each data stream over one or multiple physical interfaces. It works a lot like Network Slicing but in the hardware level.
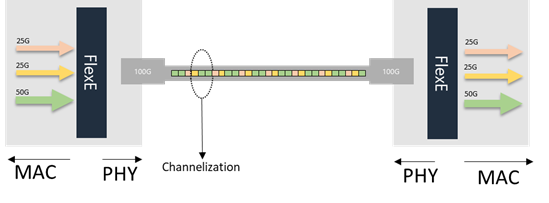
FlexE Channelization example
FlexE Applications and Benefits for Service Providers
With Bonding, Sub-rating and Channelization, FlexE offers more flexibility while using the Ethernet and provides tools for service providers to optimize their network configuration. Here are some examples that show how different service providers can apply and benefit from FlexE.
1. Wholesale service provider
Wholesale services provide network infrastructure to various tenants such as enterprise and network operators. It is important to ensure data security and data isolation.
FlexE Channelization isolates the traffic for each of the tenants so that a single physical interface can be used to service multiple customers. The bandwidth could also be configured dynamically in 5Gbps chunks, which help service providers allocate bandwidth efficiently.
2. Data center service provider
Data Center Interconnect (DCI) is getting crucial with the emergence of cloud-based services. As the demand for data grows, service providers will need higher bandwidth interconnection between data centers. And since the deployment of fiber is costly, optimizing the utilization of each fiber is very important for data center service providers.
FlexE Bonding combines multiple lower data rate interfaces into a higher rate pipeline. Data center service providers won’t need to wait for new Ethernet rates to be defined and can stay up to pace of data growth.
Another benefit brought by bonding is lower TCO. Lower data rate equipment is normally more cost effective; the cost to setup two 400GE links will be less than one 800GE link. Re-utilizing existing equipment could also avoid the extra effort to test and certify new equipment.
FlexE Channelization fills up the physical interface with channels carrying lower rate stream. Data from different clients could be carried together to optimize the link utilization.
3. Telecom service provider
Compared to DCI, telecom transport networks are much more diverse when it comes to bandwidths and utilization. Different field conditions will require different bandwidths to be used within the optical transport. Additionally, with Coherent technology, even more variations are introduced due to the optical transport leveraging different modulation schemes to deliver data in different rates for optimizing transport distance.
Since Ethernet is a fixed rate technology, it is difficult to align bandwidths from the optical transport with the port speeds available. By leveraging FlexE’s Sub-rating, operators could dynamically adjust the data rate to fit the transport network’s rate.
Network service reliability is very important to telecom service providers. Multiple mechanisms of protection are used to ensure service continuity and quality of service. FlexE Bonding not only provides higher bandwidth, but also enables network redundancy by grouping multiple interfaces into a logical interface. When one interface fails, the others could still provide service with lower rates.
Network slicing is a key feature in 5G era to enable customized services to serve different types of applications over a common physical infrastructure, such as high volume connections from IoT devices, low latency communications for autonomous driving and high bandwidths for online streaming. FlexE Channelization can support these services by separating different traffic in the physical layer and provide Hard Slicing, which guarantees resource isolation and quality of service.
FlexE Enabled Equipment
FlexE is built upon the Ethernet standard and extends its capability to support more use cases. It can work with existing cables and transceivers. FlexE equipment can also be introduced to the network with minimal architectural changes since a they are compatible with existing FlexE-unaware transport infrastructures.
UfiSpace S9510-28DC is based on Qumran2a platform with 24x25GE, 2x100GE, and 2x400GE interfaces. It supports FlexE on its 400GE interfaces and could be positioned in access networks or central offices to aggregate traffic and forward the data into a FlexE enabled transport network.
For more information about UfiSpace’s solutions supporting FlexE, please contact our sales team.
